Fundamental Units:length - 1650763.73 times the length of one emission wave of the Krypton atom,
mass - how much matter an object contains - kg ito platinum-iridium cylinder kept in a vault in France, and
time - 9 192 631 770 vibrations of a Cesium atom.
Derived Units:
SI units- Exposure, Coulomb per kilogram, C/kg, Roentgen, R, where 1 R = 2,58 x 10^-4 C/kg
- Dose, gray, Gy, rad, rad, 1 Gy = 100 rad
- Dose equivalent, sievert, Sv, rem, 1 Sv = 100 rem
- Activity, becquerel, Bq, curie, Ci, 1 Ci = 3.7 x 10^10 dps where dps is disintegrations per second
- Frequency, Hertz, Hz, cycles per second, cps, 1 Hz = 1 cps
Similar Triangles - have the same angles and the ratio of their sides is equal
Similar triangles are often used to calculate the object size with a known image size
Image = do/SOD = di/SID orI
mage = object size / source object distance = image size / source image distanceUsed mainly to calculate the size of the image
where,
do = 10cm, SID = 100 cm, SOD = 80 cm, di = ?
- do/SOD = di/SID
- 10/80 = di / 100, di = 10/80 x 100 = 12.3 cm
Magnification: the ratio of the image size to the object size is called magnification. Large Magnification require a short source object distance and large SID.
m=Si/So=SID/SOD
Newtons Laws of Motion:
- Newton's Law of Inertia.
- A body at rest will remain at rest and a body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force.
- Newton's Law of Force.
- The force of a body is given by its mass times acceleration. F=ma
- Newton's Law of Equal Reactions
- For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
Objects in Motion:
- s = vt, v=s/t
- v = Vo + at
- an object with a constant velocity has an acceleration of zero
Mass and Weight:
F=ma, Weight = mg, (gravity on earth 9.8 m/s^2, gravity Moon = 0 m/s^2)
Work and Energy: W= FS = kg/m^2 x m = Nm = j
Energy - mechanical
- kinetic and potential energy = 1/2 mv^2 and mgh
- law of conservation of energy = mgh = 1/2 mv^2
Momentum (p) = mv
Momentum is conserved in collisions; Mom before = Mom after or mv(before) = mv (after)
Heat - is energy of molecular motion. Heat transfer can occur through:
- conduction,
- convection and
- radiation.
Conduction is heat transfer from one end of a metal rod to the other end.
Heat transfer from the sun is radiation.
Heat transfer from fluid in motion is convection.
Convection energy is used by a fan to cool a room
Radiation is the emission of energy from a body. Radiation energy can be transferred through a vacuum and depends on the temperature of the body. Radiation is the principle means of heat transfer from x-ray anode to the tube housing.
Temperature:
Convert 50 degrees Fahrenheit to Degrees Celsius
50F = 100/180 C -32 =10 Celsius
Electromagnetic radiation. All forms of electromagnetic ration travel with the speed of light, 3 x 10^8 m/s. the energy of electromagnetic radiation is related to the frequency f by:
h= Planck's consistant ( h= 6.6 x 10 ^34 j/sec). therefore higher frequency = higher energy

Only X-rays and gamma rays have enough energy to separate one or more electrons from the atom to produce an ion pair. X-Rays and Gamma rays are classified as
ionizing radiation.
 |
Wavelength of a sine wave, λ,
can be measured between any two points with the same phase,
such as between crests, or troughs, or corresponding zero crossings as shown.
Frequency = 1 Hz = 1 cps.
Amplitude = V = fλ
Velocity of an electromagnetic radiation c = fλ where c = velocity of light at 3 x 10^8 m/s - and c=k for all electromagnetic radiation
Therefore:
E = hf = h (c/λ) If the energy is measured in keV and the wave length is measured in Angstroms (symbol Å) 1 A = 10^-10 m,
E(KeV) = 12.4 / λ (A) λ (A) = 12.4 / E(KeV)
Intensity is defined as the energy passing through a unit area. It is measured in joules per meter2. The intensity of an x-ray beam is obtained by multiplying the number of photons passing through a given area by the energy of each x-ray photon.
Radiation Units The photon fluence measures the number of photons per square meter. A more convenient measure of radiation is a measure of ionization produced in air (the exposure). The Roentgen was defined as the amount of radiation which would produce 2.58 x 10 ^-4 coulombs per kilogram of dry air.
1 roentgen (R) = 258 microcoulomb/kg (µC/kg)
Radiation DoseThe unit of dose measures the radiation energy deposited in the patients body. A grey is defined as a deposition of one joule of energy per kilogram. 1 Gy = 100 rad
Other radiations:Alpha and beta particles - natural radiation
Linear Energy TransferLinear Energy Transfer is the amount of Ionization Energy Transfer by a particle along its particle track, measured in KeV per micron. The higher the LET the greater its biological effect keV/µm.Quality FactorTo compare different sorts of radiation to each other we have to "adjust" the dose of radiation with a Quality Factor to get a "dose equivalent". 1 siervert = QF x Gray 1 rem = QF x rad
For Medical X-rays QF = 1 and the units are adjusted so that 1 R = 1 rad = 1 rem and 1 Gy = 1 Sv
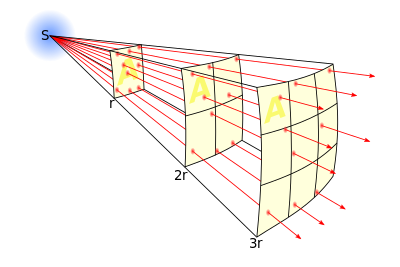 The lines represent the flux emanating from the source. The total number offlux lines depends on the strength of the source and is constant with increasing distance. A greater density of flux lines (lines per unit area) means a stronger field. The density of flux lines is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source because the surface area of a sphere increases with the square of the radius. Thus the strength of the field is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source.

where I is intensity and r is distance (radius). 1. An object moving with a velocity of 12m/s travels 48 m in 4 seconds. 2. U=4m/s, a=?, v=25m/s t=7s a=3m/s^2 |