Neuroanatomy is NB
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Thoracic inlet syndrome
- 1
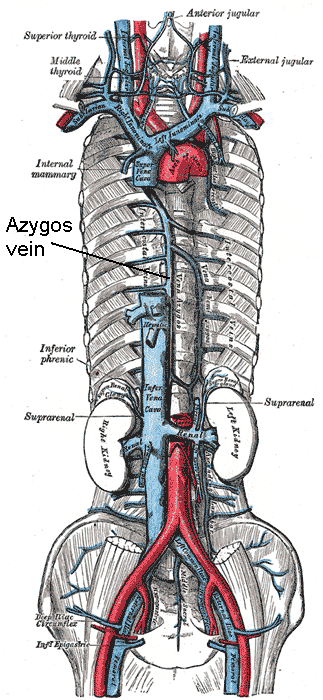
- Azygos vein at level T4
- Lable diagram cross section T4 / T3 (muscles and bones) (20)
- Trachea
- Right Vein Pulmonary Trunk
- Pretracheal Lymphnode
- 1
- Hemiazygos vein
- Branch T9 communicates with Azygos system
- Internal Thoracic artery
- Vagus nerve left
- Compare to left phrenic nerve
- 1
- Left Main Bronchus as it enters the hilus
- Vertebral Artery left
- Subclavian Artery Right
- 1
- Right Descending Coronary Artery
- Compare anatomy of all structures of the heart - table
- Moderator band
- Conduction in Right ventricle
- Infundibulum Right Pulmonary Artery
- Discuss essay - illustrate draw
- 1
- Scalenus Medius Mm - to the 2nd Rib
- Inferior Root of Brachial Plexus at T1
- Subclavian Artery Left
- 1
- Esophagus
- Caval Opening of the Inferior Vena Cava at T8
- Inferior Left Secondary Bronchus after Hilar Bifurcation
- 1
- Pectinate Muscle Rt
- Left Auricle
- Trabeculae carneae
- 1
- Middle Coronary vein

- Ventricular Septum
- Coronary Sinus
- 1
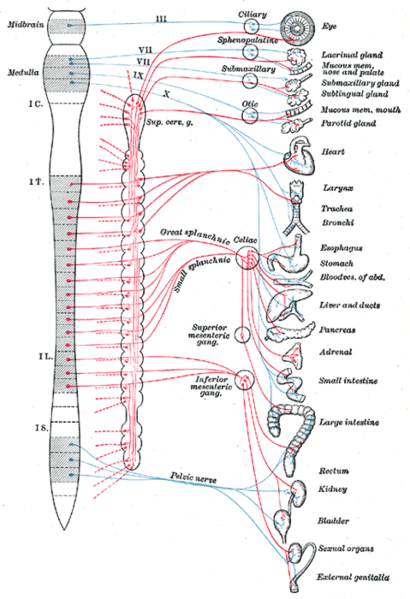
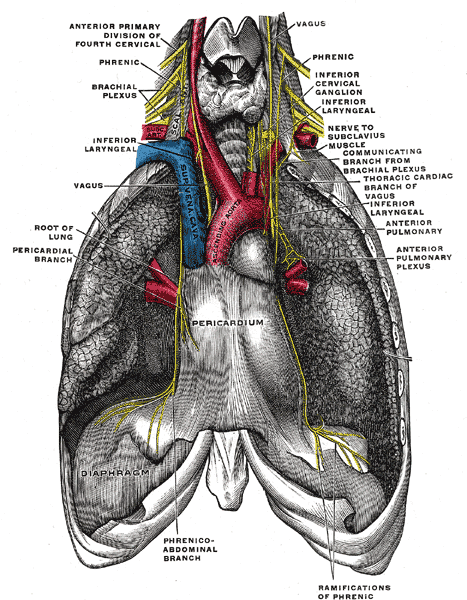
- Phrenic Nerve
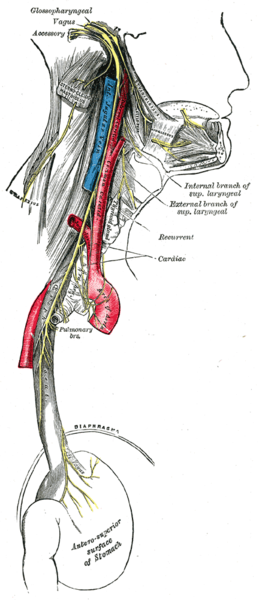
- Vagus Nerve - Recurrent laryngeal - Look at the Right Subclavian Artery with Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
- The RIGHT RECURRENT LARYNGEAL NERVE loops beneath the arch of the subclavian artery to recurr (ascend) to the larynx of which it supplies.
- Hoarseness
- Ligamentum Arteriosum (6)

- 1
- ?? Brachiocephalic Artery
- Phrenic Nerve Left
- Look for Vagus nerve
- Left Coronary carotid Artery
- 1
- Brachiocephalic Vein left over aorta
- Left Vagus Nerve
- Nn Sympathetic Chain
- Thoracic splanchnic nerves (greater, lesser, and least)
- 1
- Heart - Left Interventricular Cardiac Artery

- Papillary Muscle
- Chordae tendineae

- 1
- Mm Innermost Thoracic Muscle Left
- Nn Intercostal Nerve T9
- Nn Sympathetic Chain with branches to the Splantic Nerve
- 3x
- Left Phrenic Nerve C3,C4, C5 - referred pain to the left shoulder
- Azygos Vein
- Pulmonary Trunk
- 3x
- Vv Esophageal Veins
-
- Inferior left main bronchus
- Intercostal 5th Artery from the Aorta
- 3x
- Falciform Ligament of the Liver

- Pulmonary Vein
- Peritonium Abdomen
- 2x
- Left Scalenus anterior
- No chance in hell that we will see a subclavicular muscle - too difficult to dissect
- Nn Vagus
- 2x
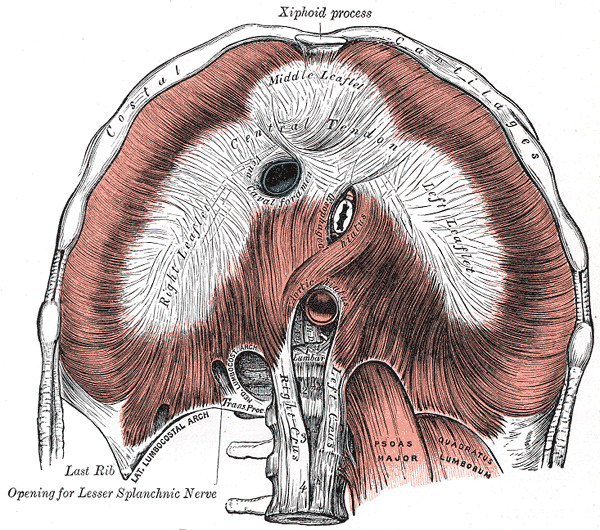
- Right central tendon of Diaphragm
- Caval opening at t8
- 3x
- Acromial end of left clavicle
- C2 odontoid process (dens) of cervical vertebra
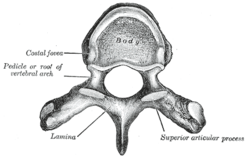
- Thoracic vertebrae
- There are no transverse foramen like the cervical vertebrae
- 1
- Rib typical - 2 articular facets
- Sternal notch
- 1st Rib left
- 1
- Xiphoid Process - T10
- Posterior arch of Atlas
- C3, C4, C5, C6 have transverse process
- 1
- C7 Transverse process
- T1
- Thoracic vertebrae
- Lumber vertebra
- 1
- Arteriogram
- Left Common Carotid Artery
- Dorsal Scapula Artery and Subcostal Artery
- Suprascapular Artery
- Anastomosis
- T2 Cross-section
- T4, T5, T10
- T4 Azygos vein

11
2 February 2011, Spot Test Anatomy
- Levator Ani Muscle, below tendinous arch
- Not the Coccygeus Muscle
- Internal Jugular Vein of the right lung, adjacent to the Aa. Common Carotid Artery
- Obturator Artery from the External Iliac Artery Aa.
- Superior Vesicular Artery
- Nn Superior Gluteal Nerve supplies the Gluteus Medius and Gluteus Minimus Muscles
- Trauma results in a waddling gate
- 2 Stations
- Round Ligament
- Stomach cross section - this is the only cross section of the abdomen
- 2 Stations
- Vv Azygos
- Superficial Vesical Artery
- 2 Stations
- Seminal vesicles
- Interventricular septum of the heart
- Dont get confused with liver
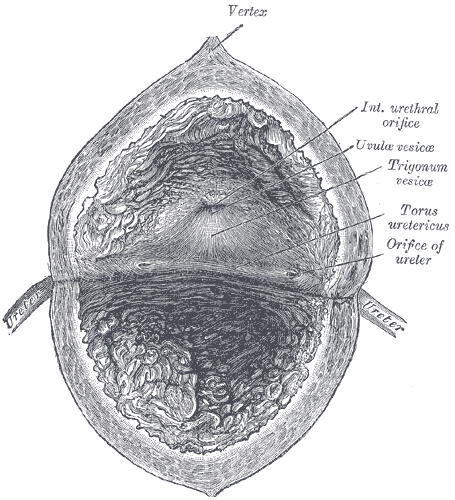
- Urethra
- Remember you dont get a membranous urethra in a female
- Testicular nerve
- how would you differentiate it from the spermatic cord structures?
- Is there a cremastic Artery?
- Nn Lateral Femoral Cutaneous
- Nn Obturator
- 2 Stations
- Ejaculatory Duct
- Prostatic ureter - where is this in relation?
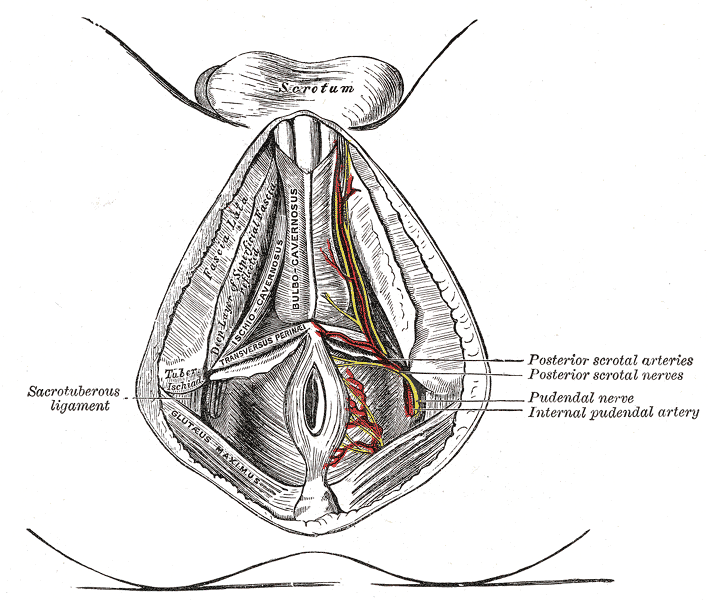
- Inferior pudendal Artery with characteristic loop back into the perineum
- Where is the inferior gluteal artery in relation to this Inferior Pudendal Artery?
- 2 spots
- Recto-uterine pouch (Pouch of Douglas)
- Puborectal sling - on cross section of Levator Ani Muscles
- The external Anal Sphincter is a bit higher
- Ischiorectal fossa or Ischioanal Fossa
- where is the rectum?
- External Iliac branch, Obturator Aa (variant)
- Looks like it was going to the bladder
- 2 sections
- External Iliac Vein
- S1 Nerve root
- Prostate - VERY IMPORTANT
- Anus
- Why not recto-anal junction?
- CT of Rectus Abdominus Muscle
- 2 x CT
- CT Seminal Vesicles
- CT Ductus Deferens
- Cervical Canal C8
- Where is the Uterine Canal? Does it exist?
 Hesselbach's triangle - Inguinal triangle
Hesselbach's triangle - Inguinal triangle- Inguinal triangle is labeled in green. The three surrounding structures:
- : Run from upper left to center.
- : Runs from upper right to bottom left.
- : Runs from upper left to bottom left, labeled rectus at upper left.
Ilioinguinal nerve - referred pain
Genitofemoral Nerve
Genitofemoral Nerve
- In human anatomy, the genitofemoral nerve originates from the upper part of the lumbar plexus of spinal nerves. Its roots are L1 and L2 (lumbar).
- The genitofemoral nerve is responsible for both the efferent and afferentlimbs of the cremasteric reflex. The ilioinguinal nerve (L1) is also involved in the afferent limb of the reflex.
- It emerges on the anterior surface of the psoas major muscle and divides into two branches:
- The femoral branch, or lumboinguinal nerve, supplies skin anterior to the upper part of the femoral triangle
- The genital branch:
- in males, it travels through the superficial inguinal ring, along with the spermatic cord, and supplies the cremaster muscle and the scrotal skin
- in females, it ends in the skin of the mons pubis and labia majora
Obturator nerve
It descends through the fibers of the Psoas major, and emerges from its medial border near the brim of the pelvis; it then passes behind the common iliac vessels, and on the lateral side of the hypogastric vessels and ureter, which separate it from the ureter, and runs along the lateral wall of the lesser pelvis, above and in front of the obturator vessels, to the upper part of the obturator foramen.Here it enters the thigh, through the obturator canal, and divides into an anterior and a posterior branch, which are separated at first by some of the fibers of the Obturator externus, and lower down by the Adductor brevis.
Femoral Nerve
?Dont have a specimen with internal??
Superior Gluteal Nerve - Waddling gate
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar