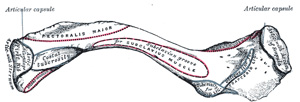
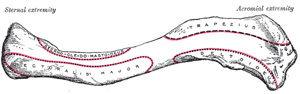
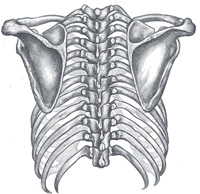
Clavicle - Is a commonly fractured bone that forms the pectoral (shoulder) girdle with the scapula, which connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton (sternum), by articulating with the sternum at the sternoclavicular joint and with the acromion of the scapula at the acromioclavicular joint.
- Has the medial two thirds tilted convex forward and the lateral one third flattened with a marked concavity.
- Is the first bone to begin ossification during fetal development, but it is the last one to complete ossification, at about age 21 years.
- Is the only long bone to be ossified intramembranously.
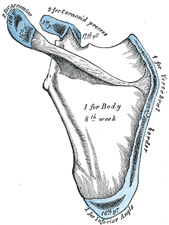
Scapula
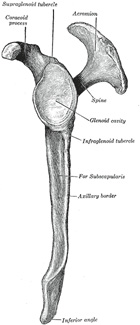
Spine of the scapula - Is a triangular-shaped process that continues laterally as the acromion.
- Divides the dorsal surface of the scapula into the upper supraspinous and lower infraspinous fossae.
- Provides an origin for the deltoid and an insertion for the trapezius.
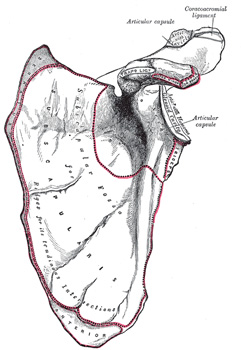
Acromion - Is the lateral end of the spine and articulates with the clavicle.
- Provides an origin for the deltoid and an insertion for the trapezius.
Coracoid process - Provides the origin of the coracobrachialis and biceps brachii and the insertion of the pectoralis minor.
- Provides an attachment site for the coracoclavicular, coracohumeral, and coracoacromial ligaments and the costocoracoid membrane.
- costocoracoid membrane definition: a strong fascia that ensheathes and extends between the subclavius and pectoralis minor muscles and protects the axillaryvessels and nerves
Scapular notch
- Is bridged by the superior transverse scapular ligament and is converted into a foramen, which permits passage of the suprascapular nerve.
Glenoid cavity
- Is deepened by the glenoid labrum for the head of the humerus.
Supraglenoid and infraglenoid tubercles
- Provide origins for the tendons of the long heads of the biceps brachii and triceps brachii muscles, respectively.
|










Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar